Hydrogel Performance Analysis: Investigating Optimal Concentrations for Water Release, Absorption, and Compression in Agricultural Applications
School Project Abstract
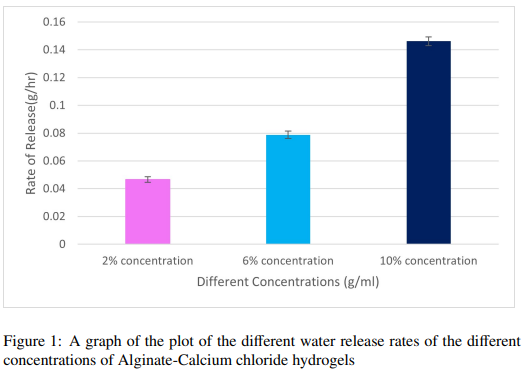
The escalating challenges of water scarcity and global food insecurity necessitate the pursuit of innovative, sustainable solutions in agriculture. This study was designed to identify the optimal hydrogel concentrations for maximizing water absorption, release, and compression, key characteristics for their effective application in agriculture, especially in helping to solve the problem of Water scarcity and global food insecurity. The approach encompassed synthesizing alginate-based hydrogels of different concentrations (2%, 6%, and 10%) and subjecting them to a series of tests to measure their rate of water release and absorption and their compressive strength. The tests were followed by extensive statistical analyses, including normality tests, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc tests, and paired t-tests, to interpret the data and draw significant conclusions. The results revealed marked differences in the performance of hydrogels at different concentrations. The 10% alginate-based hydrogel demonstrated optimal characteristics, with the highest water absorption rate and compressive strength, making it a viable candidate for agricultural applications. This study concludes that the manipulation of hydrogel concentrations directly influences their performance attributes, specifically, water release, absorption, and compression strength, which are critical for their application in agricultural practices. This understanding can significantly contribute to the development of sustainable agriculture strategies, particularly in areas prone to water scarcity.